As the logistics and supply chain sectors evolve, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) have emerged as transformative technologies within warehouse management. Imagine navigating a vast warehouse using only your smartphone or VR headset, locating items with unprecedented ease. But, as with all innovations, what challenges might arise when incorporating these avant-garde solutions? The complexities of integration, training, and infrastructure must be taken into account. Below, we delve into the various applications of AR and VR in warehouse management, highlighting their profound implications and the potential challenges that accompany them.
1. Enhanced Inventory Management
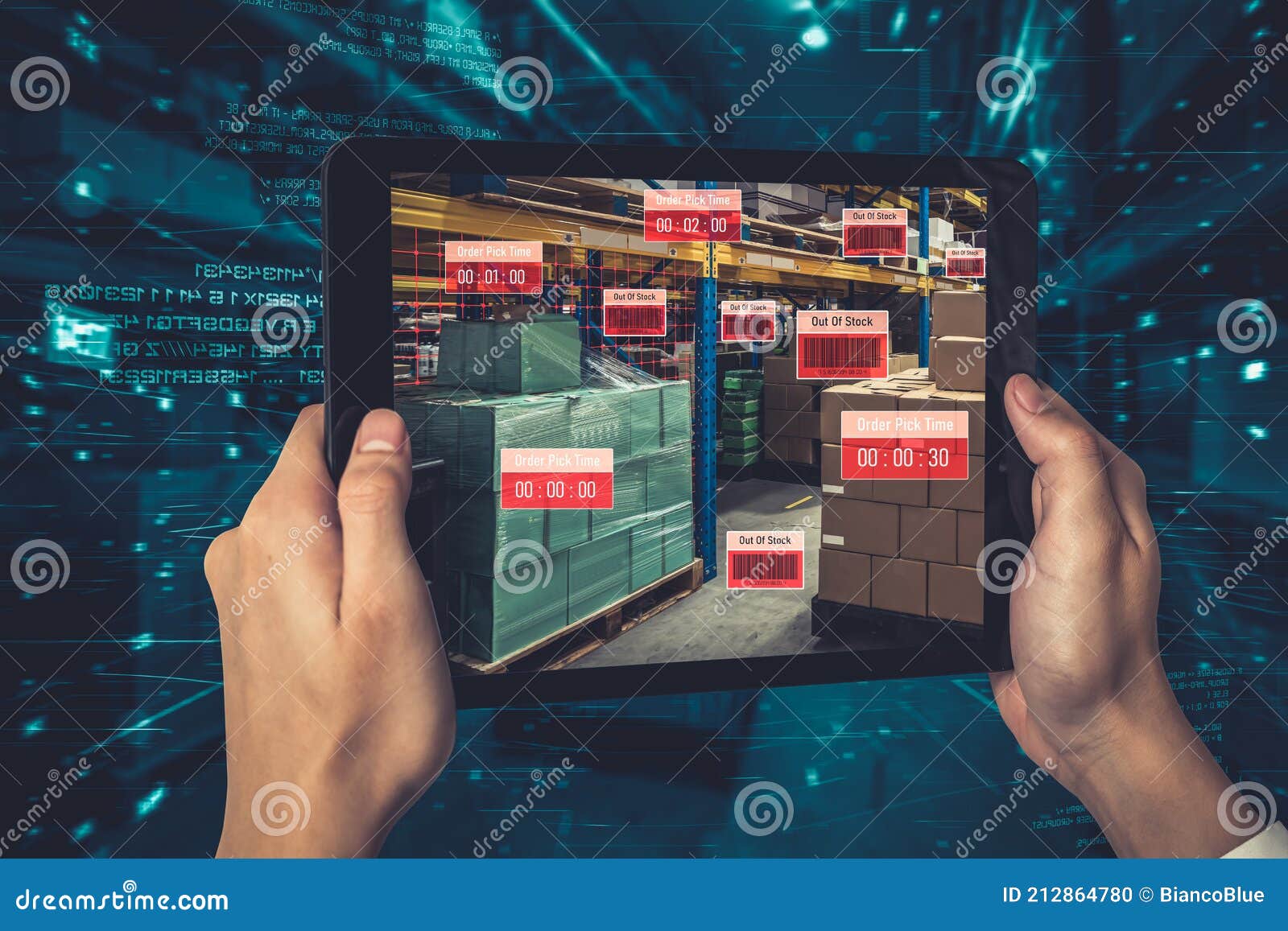
One of the most commendable applications of augmented reality in warehouse operations is its ability to revolutionize inventory management. AR systems can overlay real-time data on physical products, guiding employees to the exact location of items and providing insights about stock levels. This not only streamlines the process but also drastically reduces the likelihood of human error, which can lead to costly discrepancies.
However, implementing such technology may require significant initial investments in both hardware and software components. The challenge lies in ensuring that existing inventory management systems can seamlessly integrate with new AR applications, necessitating thorough planning and testing.
2. Worker Training and Onboarding
Another prominent application of VR in warehouse management is in employee training. Traditional training methods can often be tedious and inefficient. In contrast, VR provides a simulated environment where new employees can practice their skills without the risk of disrupting actual warehouse operations. By immersing them in realistic scenarios, and allowing them to engage with virtual tools and instructions, VR training can lead to quicker and more effective learning outcomes.
Nevertheless, VR training programs can be resource-intensive. The challenge here lies in the development of these platforms; companies must produce high-quality, engaging simulations tailored to the specific tasks their workers will perform. Balancing budget constraints while producing an effective training tool can be daunting.
3. Picking and Packing Optimization
AR can significantly enhance the picking and packing processes in warehouses. By utilizing smart glasses or mobile devices, workers can receive visible instructions combined with their real-world surroundings, directing them to the location of items that need to be picked. The technology can streamline routes through the warehouse, making the entire process faster and more efficient.
However, integrating AR into existing picking systems may come with a learning curve. Employees accustomed to traditional methods may initially resist using new technologies, presenting an implementation challenge that warehouses must navigate carefully.
4. Maintenance and Equipment Management
Implementation of AR tools extends beyond inventory and picking; it plays an essential role in equipment maintenance as well. AR can provide real-time diagnostics, overlays, and maintenance schedules directly onto existing machinery through smart glasses. Such visual aids can assist technicians in understanding faults and repairs without extensive manuals or lengthy training sessions.
The challenge, in this case, is connectivity. Warehouse environments can present obstacles for uninterrupted AR functionality, especially in large spaces with potential wireless dead zones. Ensuring all areas of a warehouse have robust connectivity is key to maximizing the effectiveness of AR applications in maintenance.
5. Collaborative Environment and Communication
AR and VR can foster enhanced collaboration within warehouse teams. For example, AR technology enables remote workers to connect with on-site employees, providing real-time visual guidance during logistical operations. This connection can assist in troubleshooting and decision-making, creating a more cohesive workplace.
However, this innovation may also give rise to issues surrounding data security and privacy. With real-time communication taking place through AR platforms, sensitive information could become vulnerable to breaches. Companies must prioritize security measures to safeguard data when employing these collaborative tools.
6. Visualization and Planning
AR and VR are also pivotal in warehouse layout planning and design. By creating virtual models of the warehouse, managers can visualize how different layouts would improve operational efficiency and space utilization. This leads to informed decision-making regarding reorganization efforts or the implementation of new processes.
Yet, the challenge lies in user acceptance. Stakeholders may be resistant to proposed changes based on virtual simulations if they struggle to grasp the technology. Facilitating understanding among all involved parties is crucial to overcoming this hurdle.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Warehouse Management
The integration of augmented and virtual reality technologies into warehouse management holds remarkable potential. From inventory optimization to training innovations, the applications are vast and varied. However, embracing these transformative technologies is not without challenges. The costs associated with implementation, the necessity for robust connectivity, and the importance of fostering acceptance among the workforce are vital considerations that cannot be overlooked.
As warehouses continue to adapt to the digital age, the judicious use of AR and VR may very well distinguish the leaders from the laggards in this competitive landscape. Is your warehouse ready to embrace this new era of operational excellence, or will you succumb to the constraints of outdated practices? The choice is yours.










Leave a Comment