For many car owners, the intricacies of automotive batteries often remain shrouded in mystery. Yet, understanding the voltage of a car battery is paramount—not merely for functionality, but for the very longevity of your vehicle’s heart. As you delve into the realm of vehicle electrics, it becomes clear that voltage is more than just a number; it’s a critical factor influencing performance, reliability, and maintenance. This exploration promises to enlighten your perspective on battery health, ensuring you can make informed decisions going forward.
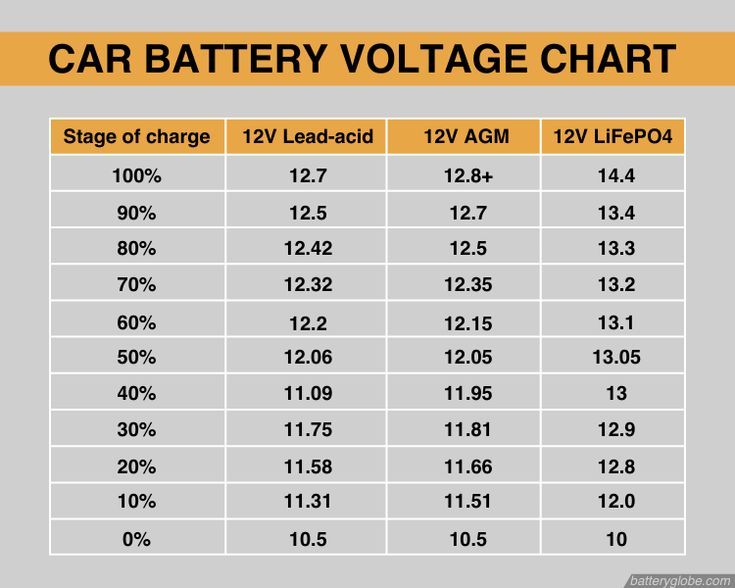
When contemplating the voltage of a car battery, it’s essential to first grasp the standard operational parameters. Most conventional automotive batteries operate at 12 volts with a crucial structural caveat: they are comprised of six cells, each generating approximately 2.1 volts. Therefore, the collective output aligns harmoniously at around 12.6 volts when fully charged. However, it’s this figure that is subject to variance, hinging on the state of the battery, ambient conditions, and overall vehicle conditions.
The ideal figure of 12.6 volts represents a fully charged battery. Below this voltage level indicates a gradual decline in electrical power, raising the specter of complications. A reading below 12.4 volts signifies that the battery is partially discharged, prompting early warning signals to any discerning owner. Strikingly, a voltage reading of 12.0 volts or below suggests a battery that is in a critical state of depletion. This can lead to sluggish starts, diminished performance, or, in dire cases, complete failure. Understanding these benchmarks allows drivers to not only anticipate potential issues but also tackle them proactively.
It’s equally important to consider the significance of cranking amps (CA) and cold cranking amps (CCA). These ratings indicate the battery’s capacity to deliver the necessary starting power at low temperatures. While voltage is pivotal, these ratings essentially define the battery’s ability to start the car. Typically, a battery with a CCA rating of 600-800 amps is sufficient for most standard vehicles operating in moderate climates. However, in regions with extreme weather, particularly frigid conditions, seeking a battery with a higher CCA becomes prudent.
Monitoring your battery’s voltage can significantly improve your vehicle’s reliability. A multimeter serves as an essential tool in this regard. Use it by connecting the leads to the respective terminals—red for positive and black for negative. A reading of 12.6 volts or higher indicates that your battery is healthy. If the voltage dips below this threshold, you may want to consider either recharging or replacing the battery. The process is straightforward: regular checks ensure you maintain optimal battery life, enhancing your vehicular experience.
Furthermore, one must consider the battery’s performance while the engine is running. During this phase, the alternator takes the reins, ideally pushing the voltage to between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. This increase not only recharges the battery but also powers the electrical systems of the vehicle. A significant drop in this voltage range during operation can herald alternator issues or internal battery faults. Such a scenario necessitates further examination or professional assistance, as ignoring the signs may eventually leave you stranded.
The relationship between temperature and battery voltage is an often-overlooked aspect. For every 10-degree Fahrenheit decrease in temperature, the chemical reactions within the battery slow down, leading to a reduction in available power. It is not just frigid winters that pose challenges; even the sultry heat of summer can catalyze electrolyte evaporation, hastening the deterioration of your battery. Maintaining a suitable environment for your battery increases its lifespan and reliability.
Given the array of advanced technologies available in modern vehicles, it is essential to recognize the shifting trends in battery systems. The advent of lithium-ion batteries has ushered in a new era. These systems often operate at higher voltages—typically around 14 volts—compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. As hybrid and electric vehicles proliferate, understanding the nuances of these different systems becomes essential for car enthusiasts and casual drivers alike. Transitioning to an electric future demands an awareness of technical specifications and their practical implications.
Battery maintenance, a topic that doesn’t receive its due focus, plays a critical role in ensuring longevity. Regularly cleaning the terminals to prevent corrosion, ensuring secure connections, and occasionally checking the water levels in non-sealed batteries can significantly enhance performance. Proper care can bolster the lifespan of the battery, allowing it to deliver optimal voltage levels over time.
Oftentimes, battery issues arise with little to no warning, which is why preventative measures and vigilant monitoring are indispensable. Regular inspections, ensuring that all electrical accessories are switched off when the vehicle is not in use, and using smart chargers during downtime can help mitigate potential failures.
In conclusion, understanding the voltage of a car battery is not merely a technicality but a fundamental pillar of automotive care and maintenance. Awareness of the ideal voltage, the implications of cranking amps, atmospheric influences, advancements in battery technology, and techniques for proper maintenance empowers drivers to foster a reliable driving experience. Cultivating this knowledge doesn’t just prolong battery life; it enhances your overall connection to your vehicle. By delving into the nuances of automotive batteries, you embark on a journey towards greater confidence and reliability in your transportation choices, ensuring smoother travels ahead.





Leave a Comment