When it comes to household pests, few creatures invoke as much dread and disgust as cockroaches. Among the various species, two of the most ubiquitous are the German cockroach and the American cockroach. While they may share the same family and are both nuisances, their behaviors, appearances, and habitats are markedly different. So, how do you distinguish between these two formidable foes? And what challenges might arise in managing their populations in your home?
This in-depth exploration will dissect the key differences between German and American cockroaches, emphasizing their characteristics, habitats, reproduction, dietary habits, and effective management strategies. By understanding what sets these two types apart, homeowners can better equip themselves to combat an infestation.
1. Physical Characteristics
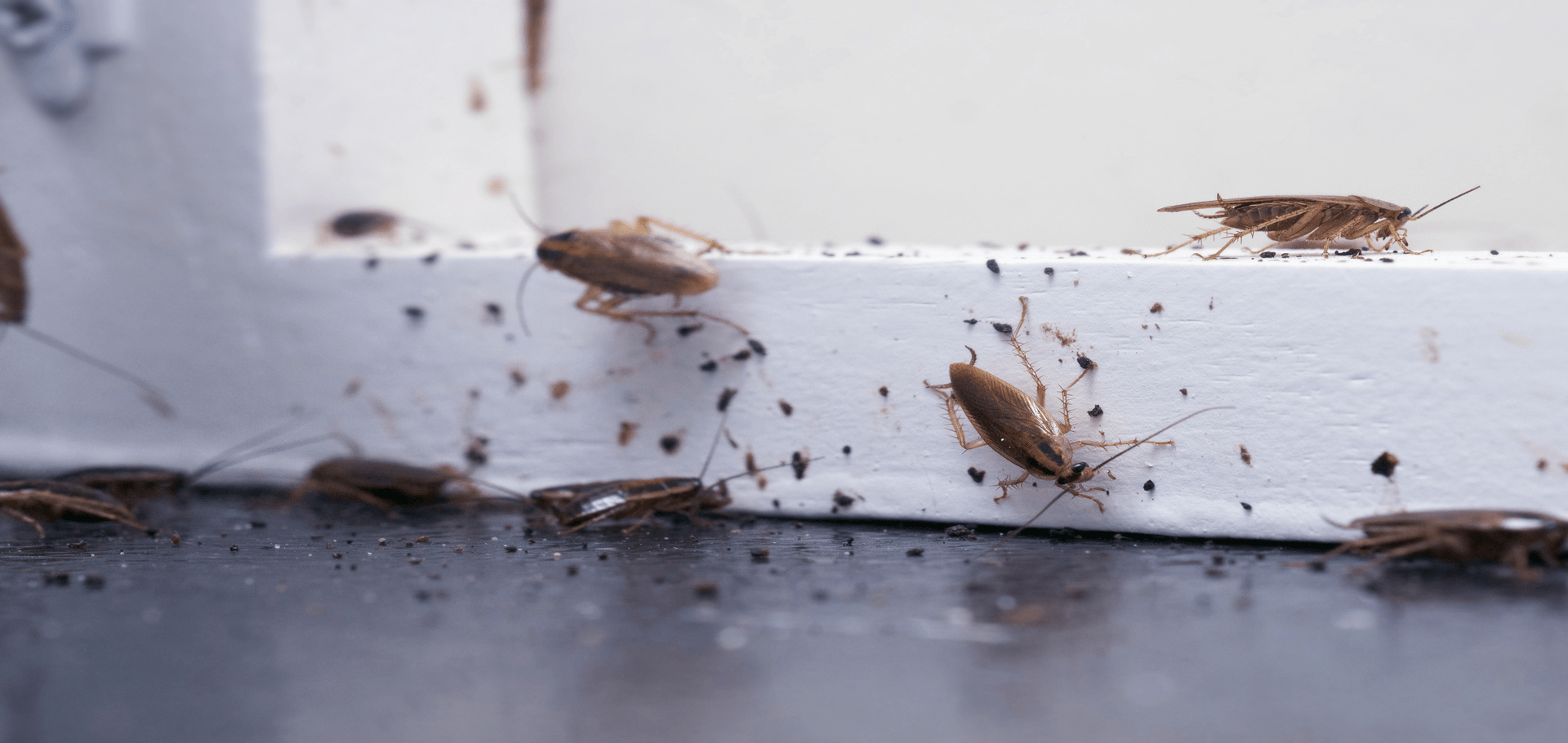
At first glance, identifying the specific type of cockroach scurrying across your floor may seem trivial, but understanding these distinctions is crucial. The German cockroach (Blattella germanica) presents with a lighter, tawny color, adorned with two dark, parallel stripes running down its back. Measuring approximately 1.1 to 1.6 inches in length, it is relatively small, making it easier to hide in inconspicuous nooks and crannies.
Conversely, the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana), one of the largest house-invading species, can grow up to 3 inches long. Exhibiting a reddish-brown hue, this roach has a lighter yellowish margin on its thorax, giving it a distinguishable outline. Its size and coloration make it less likely to go unnoticed compared to its German counterpart.
2. Habitats and Behavior
When pondering the living conditions preferred by these two species, one must appreciate their nuances. German cockroaches thrive in warm, humid environments, often favoring kitchens and bathrooms where food and moisture are abundant. Their adaptability allows them to dwell in densely populated areas, creating colonies that can explode into serious infestations within months.
American cockroaches, on the other hand, prefer a more outdoor lifestyle, often residing in basements, sewers, and drainage systems. They are more prevalent in warmer climates and can sometimes invade homes from outside sources. The behavior of each species also reflects their habitats; German cockroaches tend to be more social, clustering together in large groups, while the American roach is more solitary.
3. Reproductive Patterns
Understanding the reproductive habits of both species is critical in addressing an infestation. German cockroaches are exponentially prolific, with females producing up to 40 eggs in a single ootheca (egg case), which can hatch in just a few weeks. Given their rapid life cycle, a small population can quickly escalate to hundreds of thousands if left unchecked.
In comparison, American cockroaches may produce fewer eggs, with around 15 to 20 in each ootheca, but they have longer lifespans and can breed multiple times over their lives, contributing to a resilient population. Their slower reproductive rate means that while they can be harder to exterminate, they do not necessarily overwhelm homes as rapidly as the German species.
4. Feeding Habits
Both types of roaches are omnivorous scavengers, consuming a wide array of organic materials. German cockroaches predominantly feast on starches, sugars, and grease, which explains their affinity for kitchens. They are notorious for invading food pantries, where they leave behind a trail of contamination and potential illness.
American cockroaches, being larger, exhibit a broader dietary scope. They will eat decaying organic matter, which may include cardboard, books, and even some types of plastics. While both species can induce allergy symptoms and transmit diseases, the primary concern with German roaches lies in their ability to proliferate rapidly and contaminate food supplies.
5. Management and Control Strategies
Encountering cockroaches can indeed feel daunting, but there are effective measures to mitigate their presence. For German cockroaches, maintaining impeccable cleanliness and promptly addressing moisture issues can prevent them from establishing themselves. Baits and insecticidal gels tailored to their biology can also be particularly effective.
For American cockroaches, sealing entry points and using traps in strategic locations can help monitor and control their populations. Outdoor management, such as treating the perimeter of a home and addressing landscaping that harbors moisture, can significantly decrease their chances of invasion.
6. Conclusion: Are You Prepared?
The battle between homeowners and these resilient pests can be fraught with challenges. Understanding the differences between the German and American cockroaches is paramount for implementing effective management strategies. As these two species exhibit unique characteristics, their control measures must also be tailored to reflect their specific behaviors and habits.
As you ponder your readiness in facing these cockroach challengers, consider the proactive steps you can take. Will you fortify your defenses against the German cockroach’s rapid reproduction? Or will you strategize on fending off the robust American cockroach’s bold incursions? Knowledge combined with action can turn the tide in this perennial struggle against unwelcome guests.









Leave a Comment