Black Marks on Teeth: The Enigmatic Problem of Intrusive Stains
Teeth, often celebrated for their pearly whiteness, can sometimes betray us with unsightly black marks. These enigmatic blemishes on the enamel captivate our curiosity and elicit a plethora of questions. They not only challenge our aesthetic sensibilities but also serve as a gateway into a myriad of underlying concerns, from oral hygiene to systemic health issues. This exploration will delve into the causes, implications, and potential treatments for black marks on teeth, illuminating the multifaceted nature of this perplexing phenomenon.
Understanding the Nature of Black Marks
The appearance of black marks on teeth can manifest in various forms, ranging from faint specks to pronounced stains. These discolorations often present as a stark contrast to the typically vibrant enamel, prompting observers to inquire about their origins. Importantly, black marks are not merely cosmetic issues; they can signal deeper underlying problems that warrant attention and understanding.
Common Causes of Black Marks on Teeth
1. Tartar Build-up: One of the most ubiquitous causes of black marks is tartar, a hard calculus formed when plaque mineralizes. Neglecting routine oral hygiene can lead to the accumulation of tartar, resulting in dark stains that can be challenging to remove without professional intervention.
2. Dietary Factors: Our diet plays a pivotal role in oral health. Consuming dark-colored foods and beverages—such as coffee, tea, red wine, or berries—can contribute to external staining. Furthermore, certain condiments, like soy sauce, can leave persistent marks if the teeth are not thoroughly cleaned after consumption.
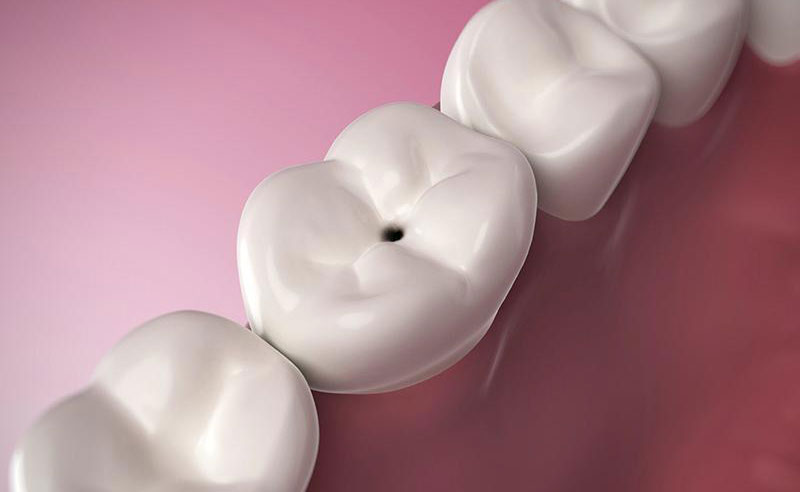
3. Tooth Decay: Dental caries, often colloquially referred to as cavities, may manifest as dark spots. As decay progresses, it can cause the enamel to weaken, resulting in discolored areas that indicate a need for immediate dental intervention.
4. Medications and Supplements: Certain medications and supplements, particularly those containing iron or certain antibiotics like tetracycline, can lead to discoloration of the teeth. These compounds can create complex reactions with the enamel, resulting in undesirable stains.
Environmental Influences
1. Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco products are notorious for staining teeth. The tar and nicotine inherent in these substances can create unsightly black marks, further exacerbated by poor oral hygiene practices among users.
2. Fluorosis: In cases of excessive fluoride exposure during childhood—when teeth are still developing—fluorosis can result. This condition may lead to dark, mottled patches on the teeth, manifesting as aesthetic concerns for those affected.
Health-Related Causes
1. Systemic Conditions: Certain systemic diseases can also precipitate changes in dental appearance. For instance, metabolic disorders may lead to abnormal enamel formation, resulting in black marks. Moreover, conditions impacting blood flow or calcium metabolism could manifest visibly on the teeth.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty or pregnancy, can affect oral health. Some individuals may notice an increase in dental staining or changes to the structure of their teeth during these periods.
Psychological and Aesthetic Considerations
It is worth noting that the perception of black marks on teeth can evoke significant psychological responses. The aesthetics of one’s smile often influence self-esteem and social interactions. Individuals burdened with noticeable stains may experience social anxiety, underlining the importance of addressing this issue promptly.
Prevention and Treatment Options
1. Consistent Oral Hygiene: The cornerstone of preventing black marks is diligent oral hygiene. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, and attending biannual dental cleanings can mitigate the accumulation of plaque and tartar.
2. Dietary Awareness: Limiting the intake of staining foods and beverages can significantly reduce the risk of discoloration. Ensuring that one drinks water after consuming such items can help wash away residual particles that contribute to staining.
3. Professional Dental Care: For existing black marks, consulting a dental professional is crucial. Options may include professional cleanings, bleaching treatments, or even restorative procedures, depending on the underlying cause.
Conclusion
Black marks on teeth are more than a superficial concern; they serve as indicators of broader oral, dietary, and systemic health issues. Understanding their origins cultivates a sense of awareness that not only fosters better dental hygiene but also underscores the interconnectedness of oral health with overall well-being. By addressing the underlying causes and pursuing effective prevention and treatment strategies, individuals can reclaim the luster of their smiles, navigating out of the shadow of black marks and into a future of vibrant oral health.








Leave a Comment