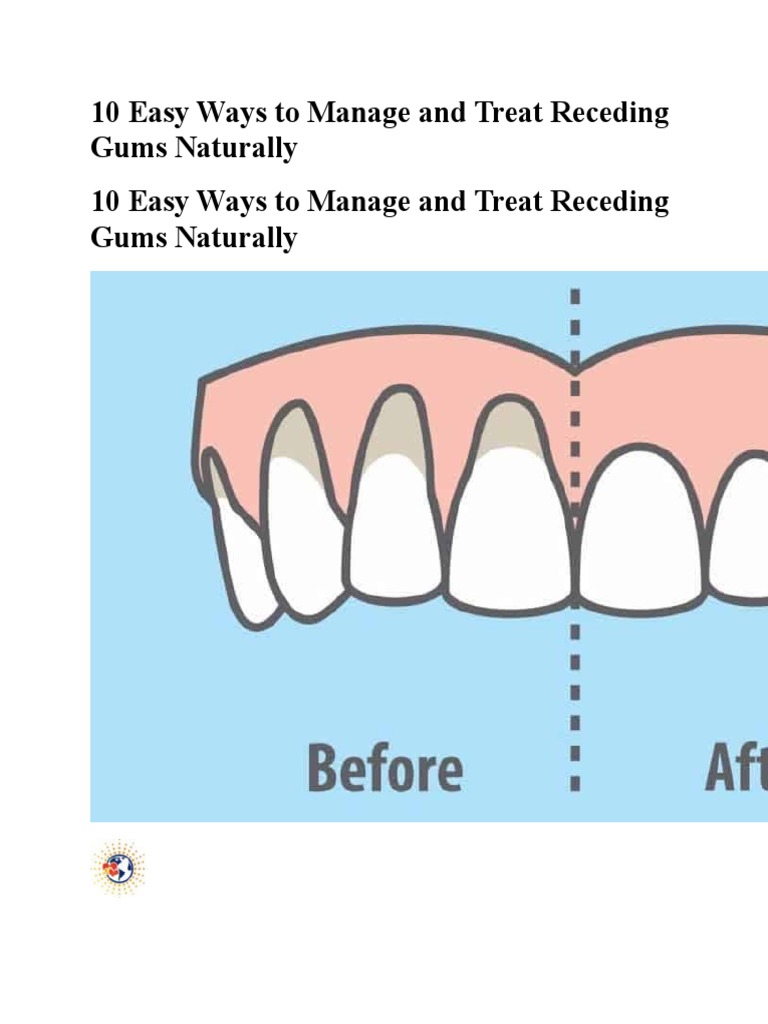
Receding gums, a dental phenomenon often overlooked, are not merely an aesthetic concern but a signifier of deeper oral health issues. This gradual erosion of gum tissue away from the teeth can lead to significant complications if left unaddressed. Aside from the superficial effects on one’s smile, receding gums can expose the sensitive areas of the tooth, making them vulnerable to decay and sensitivity. Understanding the procedures for addressing receding gums is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health and ensuring lasting vitality for your teeth.
1. Recognizing the Symptoms
Before embarking on any treatment journey, it is paramount to be aware of the symptoms that signal gum recession. Patients may observe shifts in their gum line, sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli, or increased tooth mobility. Moreover, visibly elongated teeth and the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums serve as stark indicators. Pay heed to these signs; they form the roadmap to understanding the health of your gums.
2. Understanding the Causes
The etiology of gum recession can be multifactorial. Genetic predispositions play a significant role, as certain individuals may have a hereditary tendency to experience this condition. Moreover, aggressive brushing techniques can exacerbate tissue wear, compounding the problems. Additionally, periodontal disease, nicotine use, and hormonal fluctuations can contribute to the deterioration of gum health. Emotional stress, often an overlooked aspect, may also play a role as it can incite bruxism, applying undue pressure on the gums.
3. Initial Assessment: Dental Consultation
Once symptoms have been recognized, the first course of action should be to schedule a comprehensive dental consultation. A dentist will conduct a thorough examination, often including periodontal charting to assess the depth of any gum pockets. Digital imaging may also be employed to evaluate bone and tissue health beneath the gums. This diagnostic phase is pivotal, serving as a foundation for subsequent treatment strategies.
4. Non-Surgical Interventions
In many scenarios, non-surgical approaches can be highly effective in managing receding gums. Professional dental cleanings are instrumental in removing plaque buildup, which can exacerbate gum disease. Dentists may also recommend antimicrobial mouth rinses to reduce bacterial counts in the oral cavity, contributing to overall gum health.
Additionally, a personalized oral hygiene regimen is crucial. Patients might be advised to switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush to mitigate tissue trauma and to consider employing a gentle brushing technique. Flossing, often neglected, should be performed with care to maintain the health of the gum line.
5. Surgical Procedures: When Non-Surgical Options Are Insufficient
In cases where non-surgical measures fail to yield adequate improvement, various surgical interventions may become necessary. One widely recognized technique is gum grafting, where tissue is taken from another site in the mouth or a donor site and placed over the receded areas. This procedure not only aids in aesthetic restoration but also re-establishes protective gum tissue around the teeth.
Another option is guided tissue regeneration (GTR), which employs barrier membranes to promote the growth of gum tissue over exposed tooth roots. This innovative approach is particularly advantageous for patients suffering from significant periodontal issues.
6. Periodontal Maintenance: The Road to Recovery
Following any form of treatment, rigorous periodontal maintenance is essential. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to monitor changes and identify potential complications early. Additionally, patients may benefit from professional cleanings every three to four months, acting as a preventive measure against future recession.
The adoption of modified oral care practices at home should not be overlooked. Tailoring brushing and flossing techniques in line with a dentist’s recommendations can significantly bolster gum health. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, notably vitamin C and calcium, can also support gum tissue integrity.
7. Lifestyle Modifications: A Holistic Approach
In the quest to prevent further gum recession, embracing certain lifestyle changes can yield dividends. Quitting smoking, known to impede blood circulation and delay healing, is paramount. Additionally, stress management techniques, including mindfulness practices and regular physical activity, can enhance overall well-being and indirectly aid in oral health preservation.
8. Ongoing Research and Innovations
The field of dentistry is ever-evolving, with ongoing research leading to innovative treatments that address receding gums. Advancements in regenerative techniques and biomaterials promise to enhance the effectiveness of treatments. Awareness and education play pivotal roles in the adoption of new methodologies, enabling patients to make informed decisions about their oral health.
Conclusion
In summary, receding gums serve as a window into one’s overall oral health. Addressing this condition requires a multifaceted approach, intertwining professional guidance with personal commitment to maintaining optimal hygiene and lifestyle choices. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and the range of treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their gum health and, ultimately, their quality of life. Investing in gum health is not merely a cosmetic endeavor; it’s a commitment to holistic wellness.








Leave a Comment