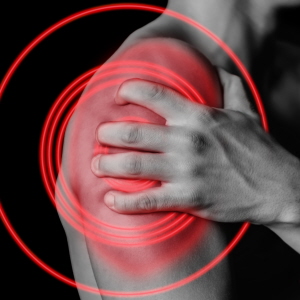
Burning pain in the shoulder can manifest in myriad ways, igniting curiosity and concern in equal measure. For many, this sensation is not merely an irritation, but rather a perplexing enigma that demands closer inspection. By navigating through the intricacies of shoulder anatomy, potential causes, evaluation methods, and treatment options, one can foster a profound understanding of this ailment, transcending initial discomfort and unlocking possibilities for relief.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Shoulder
The shoulder is a marvel of biological engineering, composed of bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles that afford remarkable range of motion. The three main bones—the humerus, the scapula, and the clavicle—work in concert through a complex system of joints, including the glenohumeral joint and the acromioclavicular joint. Upon this intricate framework rests a multitude of tendons and muscles, the rotator cuff being particularly vital. This combo of structures enables the shoulder to perform dynamic movements, yet also renders it susceptible to a spectrum of ailments, including the burning sensation that several individuals encounter.
Common Etiologies of Burning Pain
When delving into the realm of causation, numerous possibilities arise, each contributing a unique flavor to the burning experience. Among the more common culprits are:
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons within the shoulder can give rise to localized burning pain, particularly during overhead movements. This is often seen in individuals who engage in repetitive activities.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Strains or tears in the rotator cuff can lead to acute agonizing sensations, often exacerbated by specific motions, thus rendering one’s daily activities cumbersome.
- Bursitis: The bursa, a small sac filled with fluid that reduces friction, can become inflamed, leading to a discomforting burning sensation that may radiate into the upper arm.
- Nerve Entrapment: When nerves in the neck or shoulder become compressed, they may produce sharp, burning pain that travels down the arm, a phenomenon commonly attributed to conditions such as thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Cervical Radiculopathy: Issues originating in the cervical spine can manifest as shoulder pain, particularly if a nerve root is pinched. The resultant pain can evoke burning sensations accompanied by numbness or weakness in the arm.
Assessing Your Symptoms
Understanding the intricacies of burning shoulder pain necessitates careful analysis of accompanying symptoms. A multifaceted approach allows one to establish a clearer picture of the condition. Notably, it is important to discern whether the pain is:
- Localized or Radiating: Localized pain may suggest a primary shoulder condition, while radiating pain may indicate nerve involvement.
- Acute or Chronic: An acute onset may point to an injury or inflammation, whereas chronic pain may hint at degenerative changes or long-standing issues.
- Aggravated by Specific Activities: Identifying which movements exacerbate the sensation can provide invaluable insight into the underlying issue.
Assembling this information aids in structuring an informed dialogue with a healthcare professional, paving the way for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
To unravel the mystery of burning pain in the shoulder, a series of diagnostic modalities may be employed. Primarily, a thorough physical examination will allow a clinician to assess range of motion and strength, which can reveal unusual signs. Subsequently, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs can offer a glimpse into the underlying structures, helping to identify potential tears, inflammation, or degenerative changes.
In certain cases, nerve conduction studies may be warranted, especially if nerve involvement is suspected. By combining clinical findings with diagnostic testing, one can facilitate a more definitive diagnosis and form a strategic treatment plan.
Treatment Protocols: From Conservative to Interventional
The sheer range of treatment options for alleviating burning pain in the shoulder reflects the diverse underlying causes of the condition. Initial management often focuses on conservative methods:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Gradually reducing activities that exacerbate the pain can provide significant relief and foster recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in a tailored exercise regimen under professional guidance can strengthen shoulder muscles while improving flexibility and reducing pain.
- Therapeutic Modalities: Heat application, ice packs, or ultrasound therapy may be useful adjuncts, promoting healing and alleviating discomfort.
- Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help diminish pain and inflammation.
In more persistent cases, interventional treatments might be necessary:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Direct delivery of corticosteroids to the affected area can provide rapid anti-inflammatory effects.
- Manual Manipulation: Chiropractic care can assist in realigning joints and alleviating pain stemming from muscular or nerve issues.
- Surgery: As a last resort, procedures to repair torn tendons or decompress nerve roots may be considered, depending on the severity of the underlying pathology.
Conclusion: Embracing the Path to Recovery
Encapsulating the complexities of burning pain in the shoulder ultimately reveals a pathway toward understanding and treatment. By diligently recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate evaluation, and engaging in targeted therapeutic interventions, individuals can shift their perspectives from frustration to empowerment. This condition, while undoubtedly challenging, holds the potential for recovery. With each step taken, the promise of relief becomes not only a possibility but a tangible reality. Embrace the journey toward wellness, for in the realm of the shoulder, knowledge indeed fosters healing.








Leave a Comment