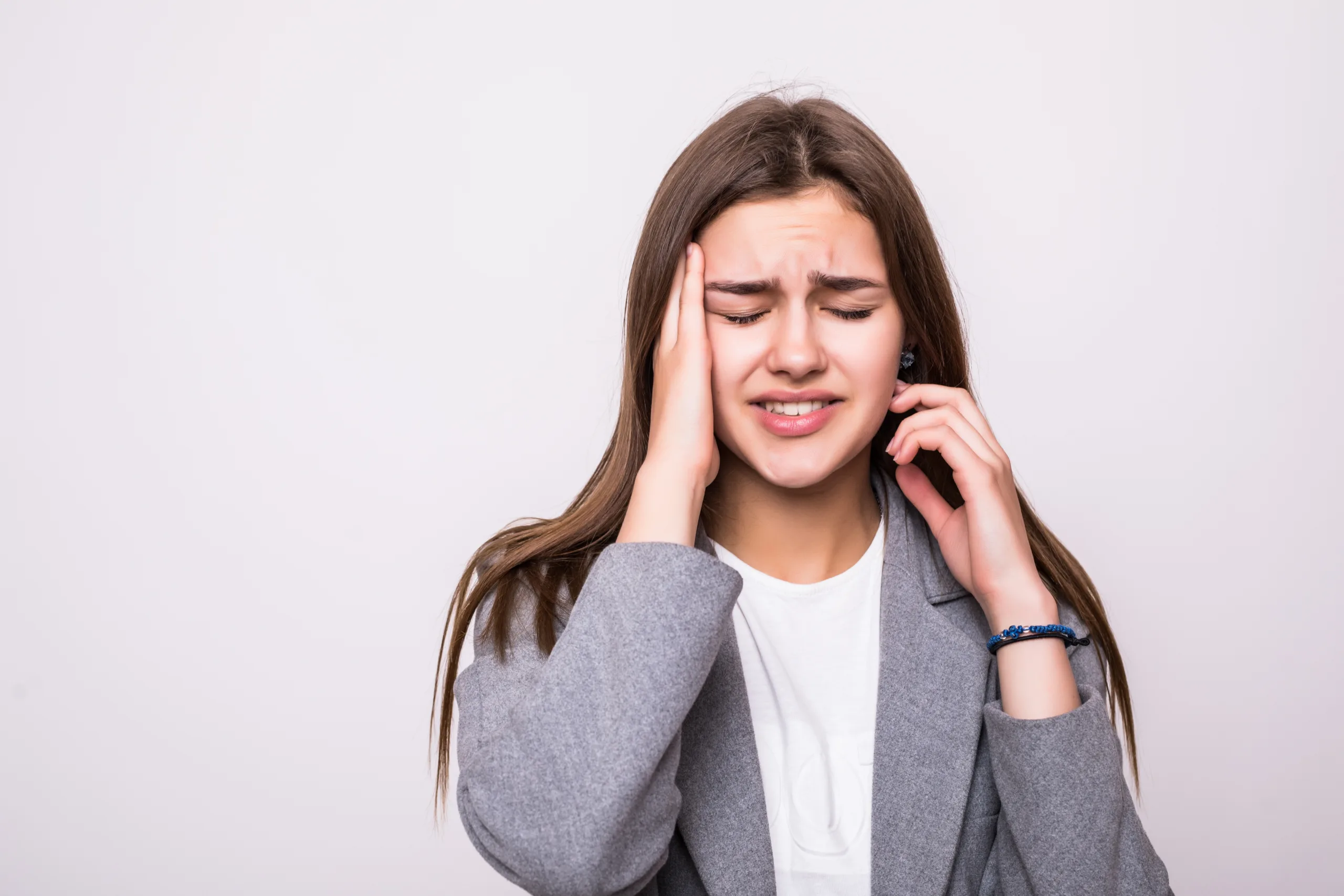
In the labyrinth of human anatomy, where intricacies unfold at every turn, must we pause and recognize a connection that transcends mere coincidence? Indeed, the dynamics of pain reveal an astonishing reality: a toothache could very well induce a headache. As cursory as this may seem at first, the interplay between dental discomfort and cranial malaise is a phenomenon worthy of exploration. Allow yourself to embark on this enlightening journey through the intertwined realms of dental health and neurological response.
To fully grasp the nexus between a toothache and headache, one must first unravel the complexities of how pain is perceived in the body. Pain, a multifaceted and often capricious sensation, can resonate in various forms and stem from myriad origins. In this case, we shall delve into the various mechanisms through which dental agony might manifest itself as headache.
Understanding the Anatomy of Pain
The head and neck region is an intricate tapestry of nerves, all of which communicate in a bewildering symphony. The trigeminal nerve, one of the principal conduits of sensation in the face, branches out like a sprawling network. It is crucial to our discussion, as it innervates the teeth and gums while simultaneously sending signals to the temporal region, responsible for headaches. When a tooth confronts decay or infection, the signals it sends out could easily propagate through this neural pathway, leading to a throbbing headache.
Dental Ailments: The Culprits of Discomfort
Several dental maladies can trigger a reverberation of pain that extends beyond the mouth. Among these are:
- Cavities: These seemingly innocuous bouts of decay can escalate into significant discomfort, sending pain signals that may spiral into a systemic headache.
- Tooth Abscess: When infection settles at the root of a tooth, the ensuing pressure and inflammation can easily bleed into cranial discomfort, creating a dual source of pain.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal ailments often incite inflammation that can radiate to adjacent regions, thereby complicating pain perception in the head.
The Cascade of Pain: Mechanisms Unraveled
Understanding the physiological mechanisms through which a toothache can manifest as a headache requires an examination of the pain pathways. When the sensory neurons in the affected tooth are activated, they send inflammatory mediators through the trigeminal nerve. This activation creates a cascade; inflammation in one area can exacerbate hyperexcitability in neighboring regions. In simpler terms, pain is contagious within the human body. A dull throb in your mouth can evolve into a crushing headache, bewildering and all-consuming.
Psychological Influence: The Mind-Body Connection
In tandem with the biochemical responses that mediate pain transmission, psychological factors also play a vital role in how we experience discomfort. Stress and anxiety, often concurrent with dental issues, can heighten one’s perception of pain. This phenomenon can create a vicious cycle: as anxiety about dental pain escalates, so too does the intensity of the headache. This psychological interplay emphasizes the importance of mental well-being in the management of physical ailments.
The Problem of Misdiagnosis
Many patients may suffer from persistent headaches without understanding their origin. In the pursuit of relief, they may seek treatment from general practitioners or neurologists, often overlooking the potent role that dental health plays in their plight. Misdiagnosis can lead to protracted suffering and unsatisfactory treatment outcomes. Only by illuminating the connection between the teeth and head can we bridge the gap towards effective solutions. Understanding the etiology of pain and correctly attributing it to dental issues may significantly influence therapeutic outcomes.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Recognizing the signs of a toothache-induced headache is pivotal. Symptoms typically include:
- Localized pain in the jaw or teeth, often sharp and stabbing.
- Intensifying sensations in the upper regions of the neck or temples.
- Episodes of throbbing pain that coincide with dental sensitivity.
If such symptoms arise, it is advisable to consult a dental professional. Timely intervention can alleviate both dental and headache-related discomfort, reinstating harmony within the afflicted individual.
Preventive Measures and Oral Hygiene
The adage “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” rings especially true in oral health. Regular dental check-ups, meticulous oral hygiene practices, and seeking prompt treatment for emerging dental issues can preclude the dual afflictions of toothaches and headaches. By bolstering one’s oral health, one not only preserves their teeth but also fortifies their entire well-being.
In closing, the intricate relationship between a toothache and a headache invites a fresh perspective on pain management. By acknowledging the connection between these seemingly disparate conditions, individuals can empower themselves to seek appropriate treatment pathways, address their concerns holistically, and ultimately eradicate the cyclic torment caused by ongoing discomfort. Let this newfound understanding serve as both a guide and a beacon for those beleaguered by the dual torment of dental and cranial pain.










Leave a Comment