In the realm of household cleaning and maintenance, combating mold is a persistent challenge that many homeowners face. Mold thrives in damp, dark environments, proliferating rapidly if left unchecked. As a result, individuals often search for effective solutions to eradicate this unwanted intruder within their homes. One popular substance that emerges in the conversation is rubbing alcohol. But does rubbing alcohol truly kill mold effectively? This article delves into the intricacies of this common question, elucidating the mechanisms, effectiveness, and alternative strategies for mold removal.
Understanding Mold
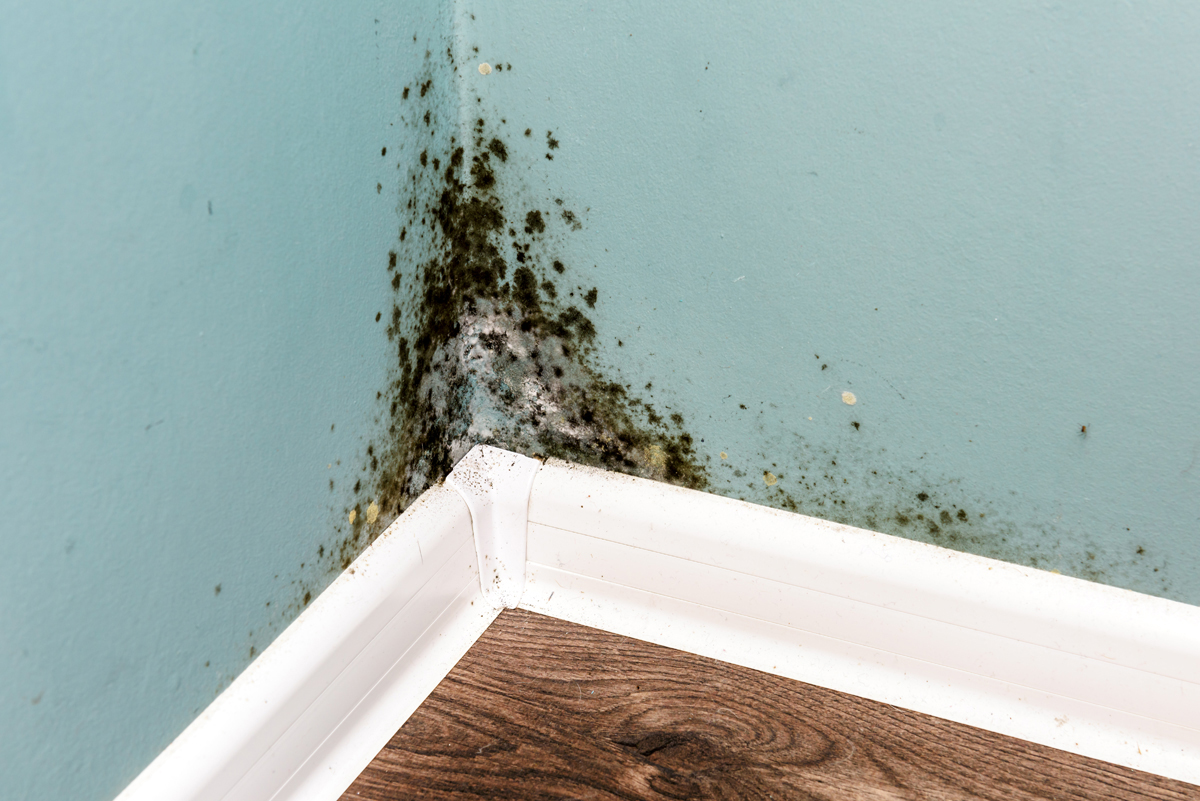
Mold, scientifically classified as a fungus, can manifest in a plethora of forms, colors, and textures. It typically flourishes in areas characterized by moisture, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. The presence of mold poses not only aesthetic issues but also health risks, particularly for individuals with allergies or respiratory sensitivities. To effectively eradicate mold, one must grasp its nature and how it interacts with various substances.
What is Rubbing Alcohol?
Rubbing alcohol, or isopropyl alcohol, is a versatile chemical compound known for its antiseptic properties. Its commonly used concentration ranges from 70% to 99% isopropyl alcohol, making it a favored choice among cleaning agents. When applied to surfaces, rubbing alcohol exhibits strong solvent qualities that can dislodge contaminants and pathogens, including bacteria and viruses. The pertinent question arises: does it possess the same efficacy against mold?
How Rubbing Alcohol Kills Mold
Rubbing alcohol’s efficacy in combating mold stems from its ability to denature proteins and disrupt cellular structures of microorganisms. When applied to mold-infested surfaces, isopropyl alcohol can effectively destroy mold spores, halting their reproduction and growth. The dehydrating nature of alcohol also helps to create an inhospitable environment for mold’s survival.
Effectiveness Against Different Mold Types
While rubbing alcohol can be beneficial in attacking certain types of mold, its effectiveness may vary across different species. Common household molds, such as Aspergillus and Penicillium, often respond well to the application of rubbing alcohol. However, more resilient molds, such as Stachybotrys chartarum—commonly referred to as black mold—may require more robust remediation methods. Therefore, it’s prudent to recognize the limitations of rubbing alcohol as a sole solution in severe mold infestations.
Application Methods
Using rubbing alcohol to kill mold can be achieved through various application methods:
- Spray Application: Pour rubbing alcohol into a spray bottle for easy application. Spray the affected area liberally and allow it to sit for 10 to 15 minutes before wiping it clean.
- Soak Cloth Method: For larger surfaces or stubborn mold, soak a cloth or sponge in rubbing alcohol and press it against the moldy area, allowing the alcohol to penetrate and eliminate the spores.
- Combination Approach: Combine rubbing alcohol with other cleaning agents, such as vinegar or hydrogen peroxide, to enhance its effectiveness. Test on a small area first to ensure compatibility.
Limitations of Rubbing Alcohol
Despite its advantages, rubbing alcohol does possess certain limitations. Its rapid evaporation rate can hinder prolonged effectiveness, especially in humid environments. Furthermore, while rubbing alcohol may kill surface-level mold, it may not penetrate deeply into porous materials such as drywall or wood, where mold roots may remain. Thus, in cases of extensive mold growth, a comprehensive remediation strategy is essential.
Alternative Mold Removal Solutions
For those considering alternatives to rubbing alcohol, several options are available:
- White Vinegar: Known for its acetic acid content, white vinegar is effective against a wide range of mold species. Its antifungal properties can help inhibit mold growth while being less harsh than chemical-based solutions.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: This oxygen-rich compound serves as a potent mold killer. Typically used in concentrations of 3% to 10%, hydrogen peroxide can penetrate porous materials and effectively eliminate mold spores.
- Commercial Mold Removers: Specialized products designed for mold remediation are available on the market. Many contain powerful fungicides, making them effective for severe infestations but may come with safety concerns due to toxic ingredients.
Safety Precautions
When using rubbing alcohol or any other chemical agent for mold removal, safety should remain a priority. Ensure proper ventilation in the area where mold is being treated. Utilize protective gear, such as gloves and masks, to prevent skin irritation and inhalation of fumes. Additionally, storing rubbing alcohol away from flammable materials is crucial due to its highly flammable nature.
Conclusion
In summation, rubbing alcohol can indeed kill mold, especially when dealing with certain types, particularly on non-porous surfaces. However, its effectiveness might diminish when faced with resilient species or deeper infestations. Recognizing its limitations and supplementing its use with alternative solutions can provide a more robust approach to mold remediation. Ultimately, maintaining a dry, well-ventilated environment is the most effective strategy to prevent mold from taking root in the first place.








Leave a Comment