Introduction
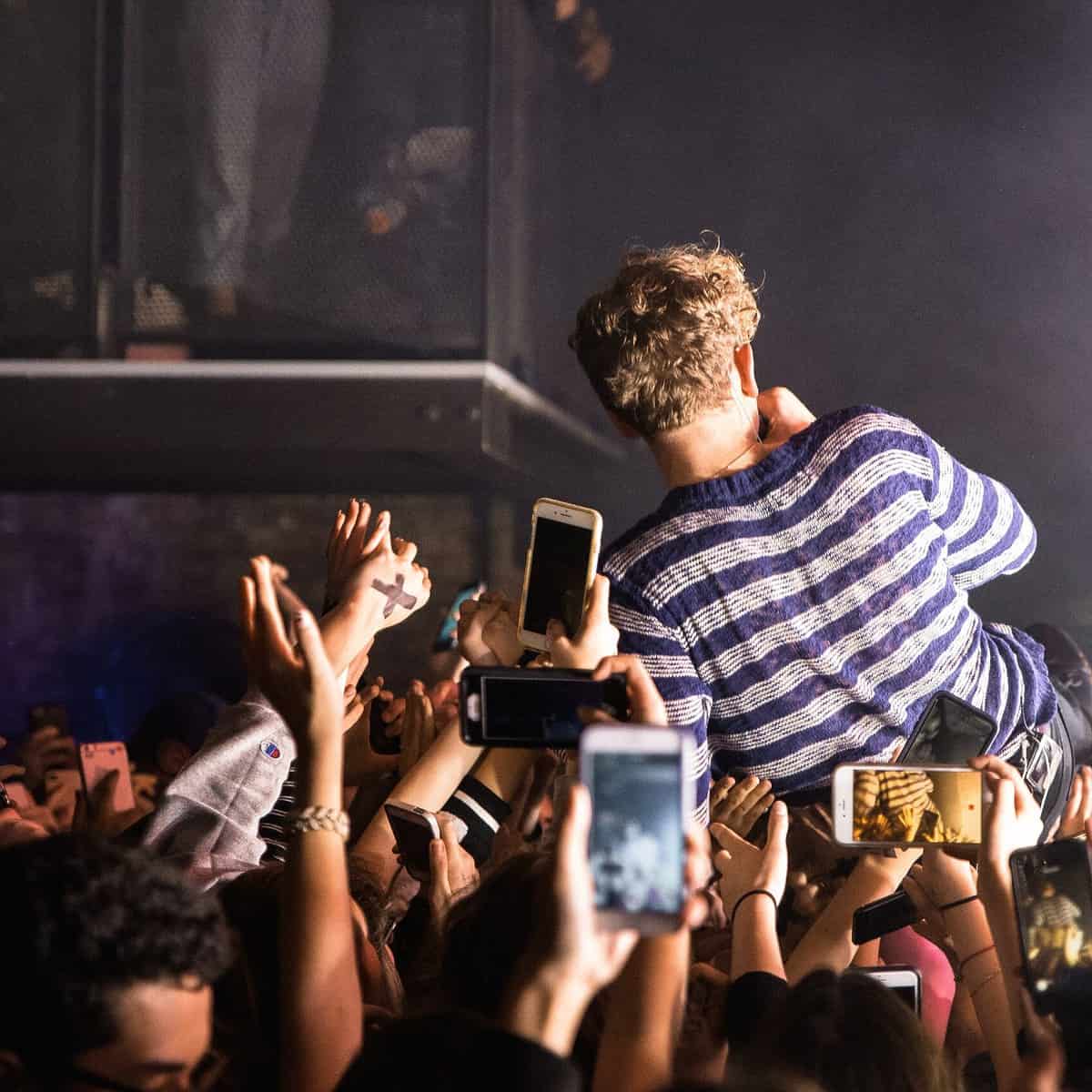
Experiencing ringing ears after attending a concert is a common phenomenon, yet it can be an alarming and disconcerting sensation. Known medically as tinnitus, this auditory symptom can range from a mild annoyance to an overwhelming sound that disrupts daily life. Many individuals are unaware of the intricacies underlying this phenomenon, which can include various factors such as sound intensity, individual susceptibility, and even the environment in which the music is experienced. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, prevention, treatment options, and long-term implications of experiencing ringing ears after a concert, offering you a holistic understanding of this perplexing condition.
Understanding Tinnitus
Tinnitus, defined as the perception of sound when no external sound is present, can manifest as ringing, buzzing, or hissing. This auditory perception is not a disease per se but rather a symptom indicative of an underlying condition. Tinnitus can be transient or chronic, depending on various factors, including exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or even stress. Concerts, with their high-decibel environments, often serve as a catalyst for temporary tinnitus episodes.
Causes of Tinnitus Following Concerts
Several elements contribute to the onset of tinnitus after a concert. Here are the primary culprits:
- Sound Intensity: Concerts frequently expose attendees to sound levels exceeding safe thresholds, often reaching upwards of 120 decibels. This exposure can induce temporary auditory trauma, leading to ringing ears.
- Duration of Exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud music can exacerbate the risk of developing tinnitus. Even brief attendance at an extraordinarily loud concert can result in auditory discomfort or ringing.
- Individual Sensitivity: The susceptibility to tinnitus varies from individual to individual. Some people have a genetic predisposition that renders them more vulnerable to auditory damage and tinnitus.
- Acoustic Trauma: Sharp or sudden loud sounds, such as a drum hit or a high-pitched note, can cause immediate ringing as they may damage the tiny hair cells within the cochlea of the inner ear.
- Pre-Existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing hearing impairments or ear conditions may find themselves more susceptible to experiencing tinnitus after attending a concert.
Symptoms Accompanying Tinnitus
The hallmark symptom of tinnitus is the ringing sound itself; however, other auditory perceptions often accompany it. These may include:
- Buzzing or Hissing: Some individuals describe their experience as a continuous buzzing or hissing sound, which can vary in intensity.
- Hearing Loss: Temporary or permanent hearing loss may accompany the tinnitus, as exposure to loud sounds often adversely affects overall auditory capability.
- Difficulty Concentrating: The presence of persistent ringing can hinder focus, making it challenging to engage in conversations or perform tasks requiring auditory attention.
- Emotional Distress: For some, tinnitus leads to heightened anxiety or frustration, particularly if it disrupts sleep or daily activities.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing tinnitus, particularly in the context of concert attendance, involves several practical strategies. Consider the following suggestions to safeguard your auditory health:
- Use Ear Protection: High-fidelity earplugs are designed to diminish sound intensity without distorting audio quality. Wearing these can significantly reduce the risk of developing tinnitus post-concert.
- Limit Exposure: Taking breaks away from the loudest sections of the crowd can provide relief for your ears. Step outside or to a less intense area if the sound becomes overwhelming.
- Prioritize Volume Levels: If you are using personal listening devices, ensuring reasonable volume settings can help protect your hearing in everyday situations, reducing your baseline risk of experiencing tinnitus.
- Be Mindful of Frequency: Regularly attending concerts at excessive volume can accumulate ear damage. Consider limiting the frequency of high-decibel music events.
Treatment Options
Should you find yourself experiencing tinnitus after a concert, various treatment options are available, ranging from lifestyle adjustments to professional therapies:
- Sound Therapy: Using ambient sounds or white noise can mask the ringing, providing temporary relief and aiding concentration during everyday activities.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help you address and manage the emotional impact of tinnitus, equipping you with coping strategies that can make the condition more manageable.
- Consult an Audiologist: Seeking advice from an audiologist can be beneficial. They may recommend tailored hearing protection and provide an auditory assessment to rule out underlying issues.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may alleviate associated symptoms, such as anxiety or insomnia, though it does not address the tinnitus itself directly.
Potential Long-Term Implications
While most instances of tinnitus following concerts subside within a few hours to days, repeated exposure to loud sounds can lead to chronic tinnitus, which requires more extensive management strategies. Chronic tinnitus can interfere significantly with quality of life, leaving individuals vulnerable to stress, sleep disturbances, and depression. Therefore, being proactive about your auditory health is crucial for preserving your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Experiencing ringing in your ears after a concert can be an unsettling reminder of the auditory dangers associated with high-volume music environments. Understanding the causes and symptoms of tinnitus allows for better-informed decisions regarding prevention and treatment. By employing protective strategies and being mindful of your auditory health, you can enjoy concerts while minimizing the risk of enduring this bothersome condition. Remember, safeguarding your hearing today is essential for enjoying the sounds of tomorrow.










Leave a Comment