Experiencing an exposed nerve in a tooth can be an agonizing and distressing ordeal. Characterized by acute sensitivity and debilitating pain, an exposed nerve typically indicates underlying dental issues that warrant immediate attention. Understanding the ramifications of this dental condition is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures associated with exposed nerves in teeth.
Understanding Exposed Nerves
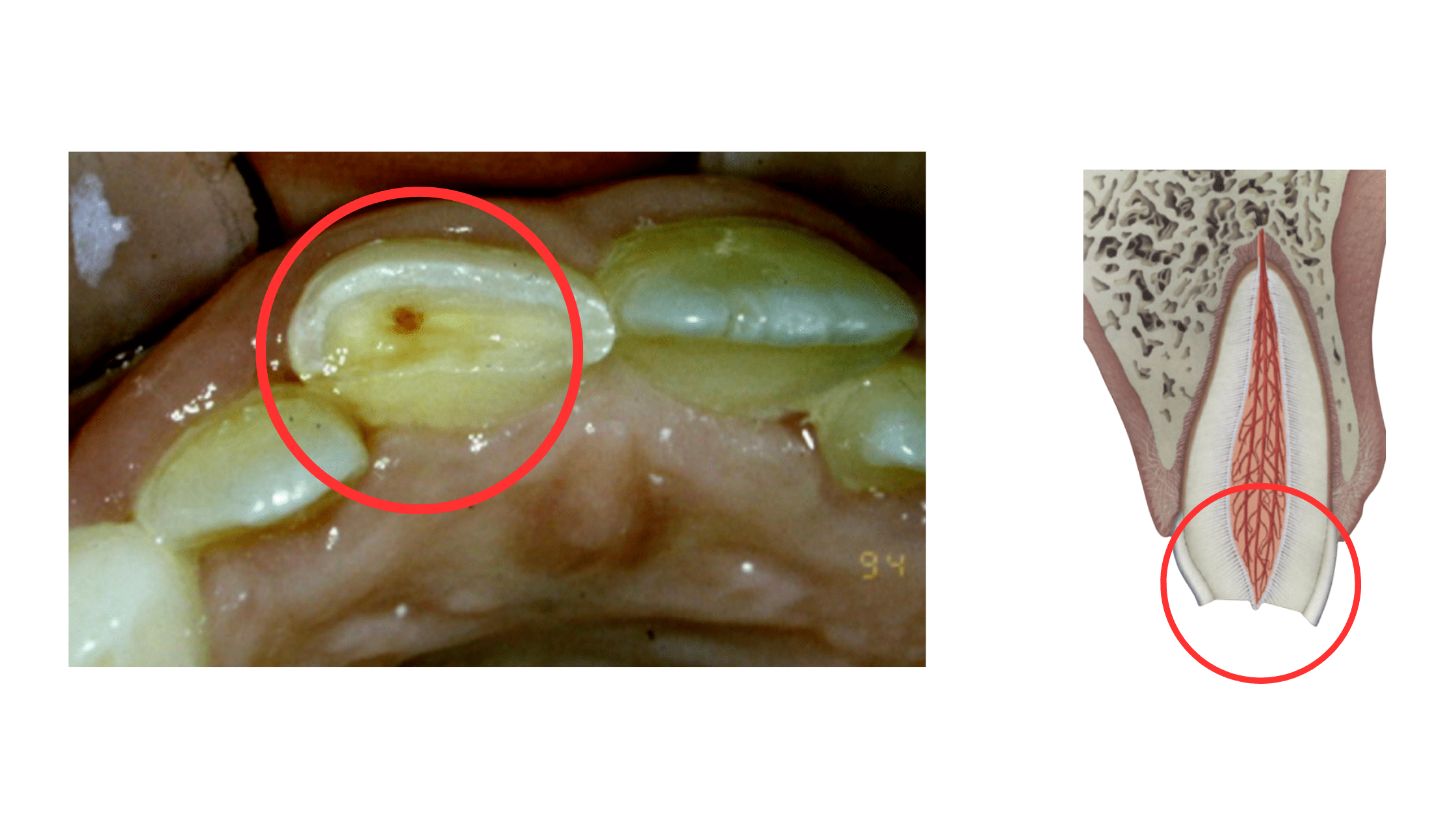
At the crux of dental anatomy lies the pulp chamber, a delicate space containing nerves and blood vessels. When the protective layers of enamel and dentin erode or become compromised, the nerve is left vulnerable, resulting in exposure. This condition can arise from various causes, including trauma, tooth decay, or gum disease.
Causes of Exposed Nerves
Several factors can lead to the unnerving exposure of dental nerves:
- Dental Caries: The relentless progression of cavities can destroy enough enamel and dentin to reveal the pulp, leading to an exposed nerve.
- Gum Recession: As gums recede, the tooth roots become exposed, which can trigger nerve sensitivity and discomfort.
- Physical Trauma: A fracture or severe blow to a tooth can dislodge or break the enamel, placing the nerve at risk.
- Advanced Periodontal Disease: Chronic gum disease may result in the deterioration of supporting structures, allowing bacteria to penetrate deeper layers.
- Tooth Grinding: Known as bruxism, this condition can wear down enamel over time, leading to nerve exposure.
Symptoms to Observe
The symptoms accompanying an exposed nerve can vary in intensity and duration. Here are common manifestations:
- Intense Tooth Sensitivity: Sudden jolts of pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet substances are hallmarks of nerve exposure.
- Ongoing Pain: Chronic, throbbing pain may occur, often worsening with time.
- Swelling and Inflammation: Occasionally, swelling around the affected tooth or gum tissues can signify an infection.
- Visible Damage: A closer look may reveal cavities or fractures, indicating the possible site of nerve exposure.
- Unpleasant Taste: A foul taste in the mouth can signal decay or infection associated with the affected tooth.
Treatment Options
Addressing an exposed nerve in a tooth typically involves a range of treatment options, tailored to the severity and underlying cause:
- Dental Filling: If the nerve is exposed due to decay, a dentist may remove the damaged area and fill it with a composite material to prevent further infiltration.
- Root Canal Therapy: In scenarios where the nerve tissue is irreparably compromised, root canal therapy might be necessary. This procedure entails the removal of the affected nerve and sealing the tooth to prevent future exposure.
- Crown Placement: For teeth that have suffered extensive damage, placing a crown post-treatment may provide additional protection and restore functionality.
- Fluoride Treatments: In cases of early decay, fluoride treatments might be utilized to remineralize enamel and reduce sensitivity.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter analgesics or prescribed medications may alleviate discomfort in conjunction with other treatments.
Preventive Strategies
Prevention remains the most effective strategy against exposed nerves in teeth. Implementing good dental hygiene practices can mitigate risks significantly. Here are proactive measures to consider:
- Routine Dental Check-Ups: Regular visits to the dentist can aid early detection of potential problems before they escalate.
- Effective Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing can help remove plaque and prevent cavities.
- Dietary Choices: Reducing sugar intake and opting for a balanced diet can significantly decrease the likelihood of decay.
- Protective Gear: If involved in contact sports, using a mouthguard can shield your teeth from physical trauma.
- Avoiding Tobacco Products: Smoking and chewing tobacco can exacerbate gum disease, leading to increased risk of nerve exposure.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when to consult a dental professional is vital. If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or heightened sensitivity extending beyond occasional discomfort, it is prudent to seek immediate dental evaluation. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications, including infections that may necessitate extensive procedures.
Conclusion
An exposed nerve in a tooth is more than just a nuisance; it is often indicative of more significant dental issues requiring attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take a proactive approach in protecting their dental health. Moreover, implementing preventive measures can greatly reduce the likelihood of encountering this painful condition. Remember, the pursuit of oral health not only enhances the quality of life but also ensures that smiles remain bright and vibrant.








Leave a Comment