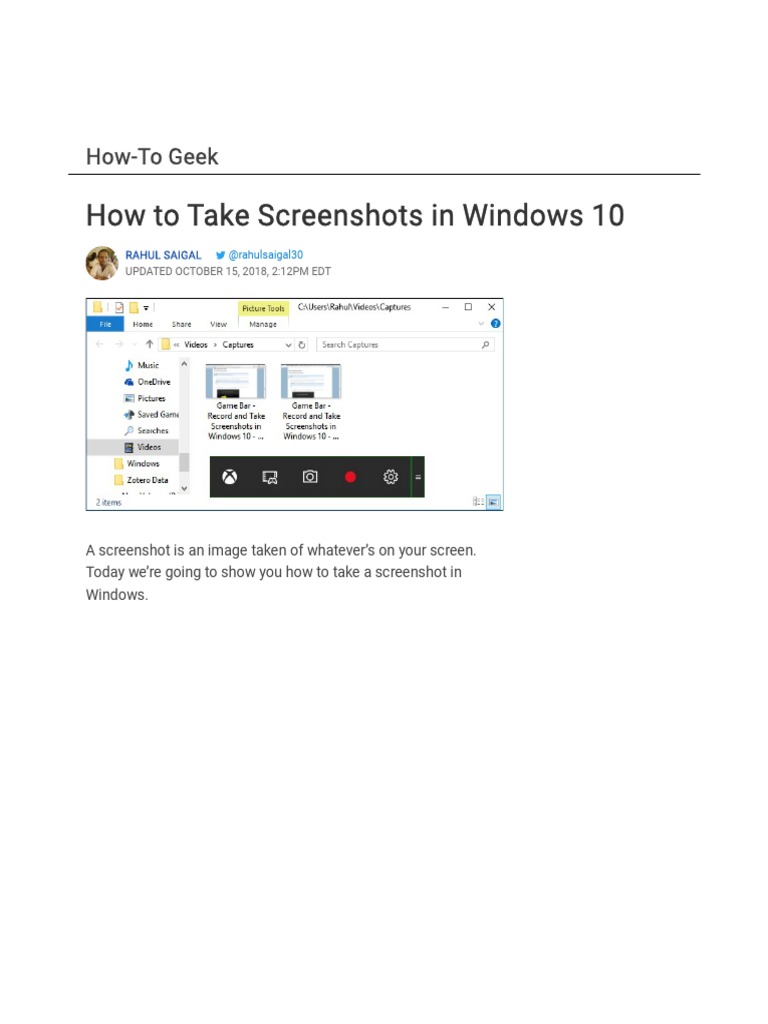
Screen printing is a captivating method of transferring images onto various surfaces, utilizing a stencil and a mesh screen to create vibrant designs. This artistic technique, deeply embedded in the fabric of contemporary culture, offers flexibility and precision while producing high-quality prints. As both an art form and a commercial process, the allure of screen printing lies in its straightforward approach and the endless possibilities it offers for creativity. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn how to successfully execute screen printing, focusing on the materials, methods, and nuances that elevate this craft.
1. Understanding Screen Printing Basics
Before embarking on your screen printing journey, grasping the foundational elements is crucial. At its core, screen printing utilizes a mesh screen stretched over a frame. This screen acts as a stencil, allowing ink to pass through only in designated areas, ultimately forming your desired design on the substrate below. The ink used in this process is typically thick and opaque, ensuring vibrant, long-lasting colors.
2. Gathering Your Materials
Essential materials are the lifeblood of any screen printing venture. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Screen Frame: Choose a sturdy frame with a mesh count suitable for your ink type and design complexity.
- Emulsion: This light-sensitive liquid is spread over the screen to create your stencil.
- Photo Exposure Unit: If you’re creating a detailed design, a light source is necessary to expose the emulsion properly.
- Ink: Select specialized screen printing ink for textiles, paper, or other materials, depending on your project.
- Squeegee: This tool is essential for spreading ink evenly across the screen.
- Substrate: The material on which you’ll be printing, such as fabric, paper, or wood.
- Cleaning Supplies: Solvents and scrapers will help you maintain your equipment.
3. Preparing Your Artwork
Your design serves as the blueprint for your screen printing project. Use graphic design software to create your image, ensuring that it’s in high resolution. Consider using bold colors and shapes, as intricate details may not translate well through the screen printing process. Once your design is complete, print it onto a transparency film, making sure to utilize a dark ink so that it blocks light effectively when exposed to the emulsion.
4. Coating the Screen
With your screen frame and emulsion at the ready, it’s time to coat your screen. In a dimly lit environment to prevent premature exposure, apply a thin, even layer of emulsion to both sides of the screen. Using a squeegee, press down firmly to achieve an even coat. Allow the screen to dry completely, ideally in a dark space, as light exposure can ruin your stencil.
5. Exposing the Screen
Once the emulsion has dried, place your transparency film onto the screen, ensuring it’s aligned correctly with the frame. Expose the screen using a photo exposure unit or a strong light source for a specified duration—this step solidifies your design onto the emulsion. The areas blocked by your design will remain soft, while the exposed areas will harden. It is essential to follow the emulsion manufacturer’s instructions for optimal exposure times.
6. Washing Out the Screen
After exposure, it’s time to wash out the screen. Rinse it with cool water to remove the unexposed emulsion. A gentle spray from the water hose can help clear away the excess without damaging the screen. Once the design is visible through the screen, let it dry completely in a dark space once more. At this point, your stencil is ready for printing.
7. Setting Up for Printing
Position the substrate beneath the screen on a flat surface or printing press. Ensure everything is aligned correctly to avoid misprints. Apply a small amount of ink at one end of the screen, then use the squeegee to pull the ink across the screen evenly. This technique helps transfer the ink through the mesh onto your substrate. Be mindful of the pressure applied; too little may cause an incomplete print, while too much could lead to smudging.
8. Curing the Print
After printing, it’s vital to cure the printed design to ensure durability. Depending on the type of ink used, heat curing might be necessary; for instance, plastisol inks require heat to set correctly. Utilize a heat press or a convection oven to reach the temperatures specified by the ink manufacturer. Proper curing will help make your print wash-resistant and long-lasting.
9. Cleaning Up
Once your prints are completed and cured, take the time to clean your tools and workspace. Scrape excess ink off your screen and squeegee, then use ink wash or solvents to clean the emulsion and mess thoroughly. Maintaining your tools not only preserves their longevity but also ensures the quality of future prints.
10. Experimenting with Techniques
After mastering the basic process, experimenting with various techniques can unlock new creative horizons. Consider trying out different inks, layering colors, or incorporating textures for unique effects. Exploring these innovative approaches will deepen your understanding of the medium and elevate your artistic expression.
Screen printing is not merely a production method; it’s an exploration into the intersection of art and technology. The meticulousness of each stage invites a profound appreciation for the craft, fostering a connection between the creator and their work. Dream, create, and embrace the exhilarating world of screen printing—an endless adventure in creativity awaits.








Leave a Comment