Maintaining optimal oral health is imperative not only for a stunning smile but also for comprehensive well-being. Among the myriad of dental issues that can arise, gingivitis stands out as one of the most prevalent yet often overlooked conditions. Recognizing its early symptoms can be crucial to preventing more severe periodontal disease. This article serves as a detailed guide to help you discern whether you might be grappling with gingivitis.
Understanding Gingivitis
Before identifying the signs of gingivitis, it is essential to comprehend what this condition entails. Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gingiva, the soft tissue surrounding your teeth. Causes are typically associated with poor oral hygiene, leading to plaque buildup that may harden into tartar. This accumulation engenders a chronic inflammatory response, which can progress if left untreated.
Early Symptoms to Note
Recognizing the early signs is critical. The following symptoms are often indicative of gingivitis:
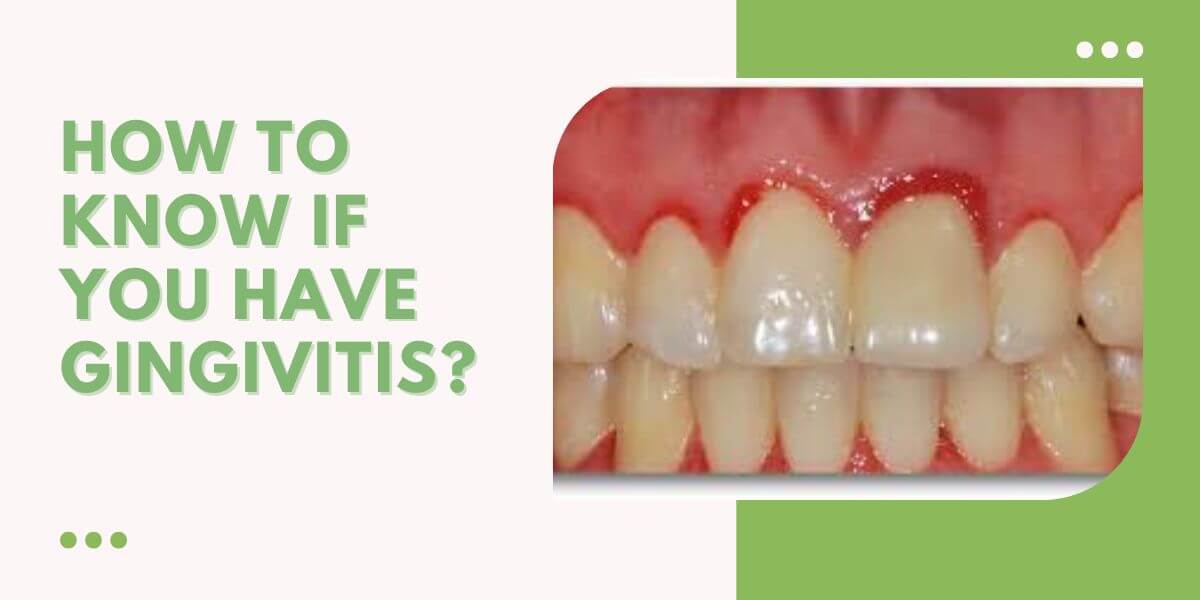
- Red or Swollen Gums: Healthy gums should appear pale pink and fit snugly around your teeth. When gums become reddened or swollen, it is often a precursor to gum disease.
- Bleeding Gums: One of the most telling signs is the presence of blood when brushing or flossing. This bleeding can range from slight to significant, depending on the severity of the inflammation.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Halitosis, or chronic bad breath, may be a subtle hint that bacteria are accumulating in your mouth due to plaque. This odor can often be difficult to eliminate with regular mouthwash or oral care techniques.
- Changes in Gum Texture: Healthy gums exhibit a firm texture. If you notice that your gums feel spongy or soft, this could signify gingivitis.
- Pus Between Teeth: Perhaps one of the more alarming symptoms, the presence of pus may suggest bacterial infection and should prompt immediate dental consultation.
Risk Factors to Consider
Being aware of specific risk factors for gingivitis can empower you to take proactive measures. Some of these include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene Habits: Neglecting consistent brushing and flossing constitutes the primary risk factor for gingivitis.
- Smoking or Chewing Tobacco: Tobacco products can inhibit blood flow to the gums, diminishing their ability to heal and increasing the likelihood of infection.
- Hormonal Changes: Women may experience fluctuations in hormonal levels during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause that make gums more vulnerable to inflammation.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet deficient in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can impair your body’s ability to combat gum disease.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases, can compromise your immune system’s ability to fend off infections, including gingivitis.
Diagnosis and Professional Evaluation
While you can identify several signs indicative of gingivitis, a definitive diagnosis must be made by a dental professional through a comprehensive examination. Dentists may use various diagnostic tools, including:
- Visual Examination: A dentist will meticulously examine your teeth and gums for redness, swelling, or any other irregularities.
- Periodontal Probing: This involves measuring the depth of the pockets between gums and teeth to assess the extent of gum recession.
- X-Rays: Dental radiographs may be utilized to observe underlying bone structure and any potential loss due to advanced periodontal disease.
Maintaining Gum Health
If diagnosed with gingivitis, treatment and management will typically include enhanced oral hygiene practices and possibly professional dental cleanings. To maintain gum health, consider the following:
- Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, ensuring that you address the gumline for optimal cleaning.
- Floss Daily: Flossing is vital in removing food particles and plaque from areas that brushing cannot reach, thus deterring bacterial growth.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule dental check-ups every six months, or more frequently if advised by your dentist.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a nutrient-rich diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to fortify gum health.
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking or tobacco will significantly improve your oral health and reduce the risk of gingivitis.
Conclusion
Gingivitis, though common, should not be dismissed as an inconsequential ailment. By understanding its signs and symptoms, you can take pivotal steps towards prevention and treatment. Early detection and adherence to good oral hygiene practices will not only save your gums but can enhance your overall health in profound ways. Foster awareness, maintain regular dental visits, and embrace a holistic approach to oral care to keep gingivitis at bay.



Leave a Comment