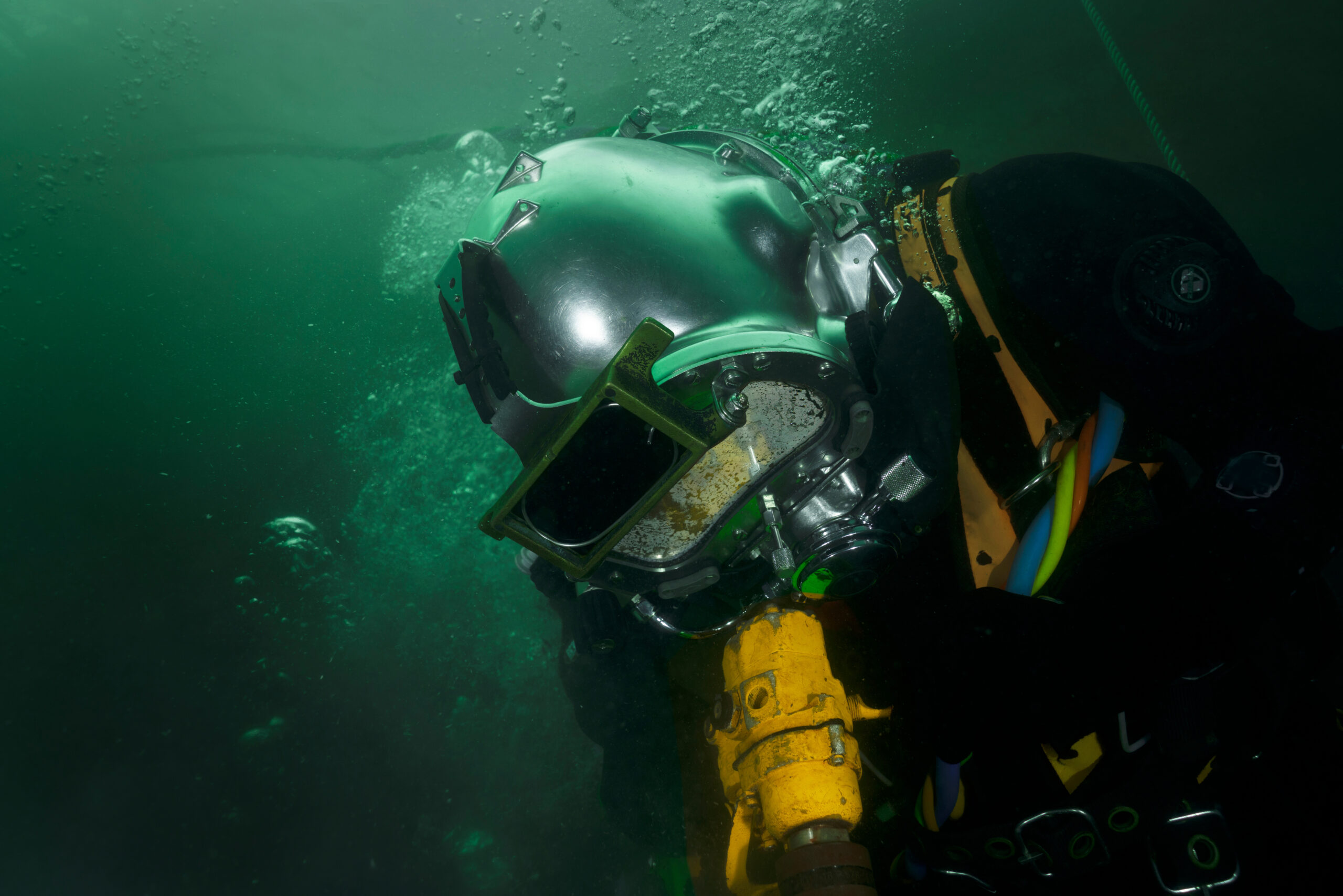
Underwater welding, a unique and specialized field, transcends conventional welding methods as it takes place beneath the surface of the water. This niche profession requires individuals to possess an array of skills spanning from advanced welding techniques to scuba diving prowess. Despite the allure of this high-stakes occupation, it’s imperative to scrutinize the underlying realities, particularly the underwater welding mortality rate, which sheds light on the associated risks and challenges.
The mortality rate among underwater welders, while not as widely discussed as that of other industrial professions, warrants serious consideration. This article aims to explore the multifaceted dimensions of underwater welding mortality, dissecting the contributing factors, preventive measures, and the broader implications for both welders and the industry at large.
1. Understanding Underwater Welding
Underwater welding can be categorized into two main types: wet welding and dry welding. Wet welding entails welding in an aqueous environment, while dry welding utilizes hyperbaric chambers to create a controlled atmosphere. Each method presents distinct challenges; however, both demand rigorous training and a thorough understanding of the marine environment.
2. The Stark Reality of Mortality Rates
While precise statistics vary, the mortality rate for underwater welders is estimated to be significantly higher than that of traditional welders. Various reports suggest that the fatality rate can be anywhere between 15 to 20 times greater than conventional welding occupations. This alarming figure calls for an in-depth examination of the precarious nature of underwater welding and the factors contributing to these fatalities.
3. Contributing Factors to Underwater Welding Mortality
Several elements contribute to the enhanced risk associated with underwater welding:
- Diving-Related Risks: Underwater welders contend with the perils of diving, including decompression sickness, drowning, and barotrauma. These factors can culminate in dire consequences, particularly in adverse conditions.
- Environmental Hazards: The underwater environment is fraught with unpredictability. Currents, visibility issues, and marine life can all pose significant dangers to welders. For example, entanglement in fishing nets or contact with venomous sea creatures can lead to life-threatening situations.
- Technical Challenges: The complexities of underwater welding techniques amplify the risks. Improper technique or equipment failure can result in catastrophic incidents. Moreover, the risk of electrical shock, given the presence of water, cannot be overlooked.
- Inexperience: A general lack of experience among new entrants into the field exacerbates the danger. Comprehensive training is crucial, but insufficient preparation can lead to tragic outcomes.
4. Preventive Measures and Safety Protocols
To mitigate these risks, the industry emphasizes the implementation of stringent safety protocols and preventative measures. Among these are:
- Rigorous Training Programs: Adequate training is essential. Programs should integrate both welding techniques and diving safety, ensuring that professionals are well-equipped to handle the demands of underwater tasks.
- Use of Advanced Equipment: Modern equipment, including dive gear and welding apparatus, plays a crucial role in enhancing safety. Regular maintenance and checks can prevent malfunctions that could prove hazardous.
- Emergency Preparedness: Welders should be trained in emergency response techniques. Quick access to rescue resources and knowledge of first aid can be lifesaving under critical circumstances.
- Health Assessments: Regular health check-ups for divers can help identify pre-existing conditions that may exacerbate risks associated with underwater work.
5. The Psychological Toll
The psychological ramifications of working in such a perilous environment are profound. The constant awareness of risks and potential dangers can lead to heightened stress levels, anxiety, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Addressing mental health in conjunction with physical safety is crucial for the well-being of underwater welders.
6. The Future of Underwater Welding Safety
Innovations in technology and safety protocols continue to evolve, promising advancements in underwater welding safety. The advent of robotic welding devices in certain applications may reduce the need for human welders in the most hazardous environments. As industries increasingly prioritize worker safety, a cultural shift toward valuing precaution and preventive measures can be anticipated.
7. Conclusion: A Call for Awareness and Action
While underwater welding presents an enticing career with its own unique allure, safety must remain at the forefront of discussions. The mortality rate associated with this profession cannot be understated, serving as a poignant reminder of the inherent hazards involved. By fostering a culture of safety, enhancing training protocols, and prioritizing mental health, the industry can take significant strides toward mitigating these risks. As we shift our perspective on this vital profession, we must pledge to prioritize the safety and well-being of those who brave the depths to uphold the essential infrastructure of our underwater worlds.










Leave a Comment