As summer approaches, the allure of sun-kissed skin becomes irresistible. Many yearn for that perfect tan; however, understanding the science behind ultraviolet (UV) rays is imperative to achieving safe, effective tanning. Tanning is not merely an aesthetic choice but involves intricate biological processes influenced by the types of UV radiation we encounter. Here, we delve into the intriguing realm of UV light to explore what conditions facilitate tanning, how it varies throughout the day, and the implications for skin health.
1. Understanding UVA and UVB Rays
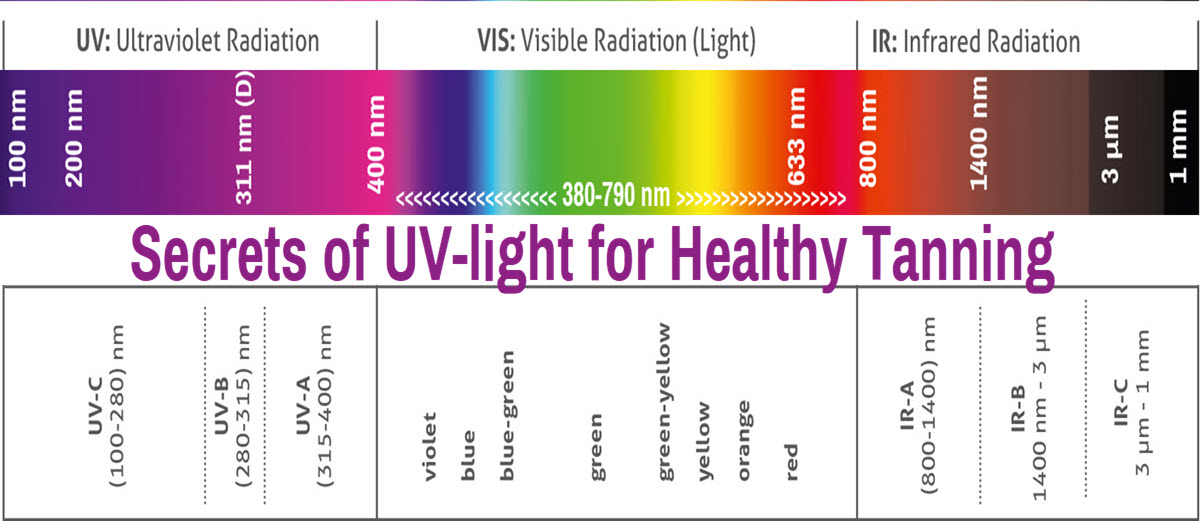
To comprehend what UV levels are conducive to tanning, one must first differentiate between the two principal types of UV rays: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate the skin more deeply and account for the majority of the tanning process. These rays stimulate melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin color. Conversely, UVB rays are primarily responsible for causing sunburn and have a more direct role in vitamin D synthesis. A proper balance of both is vital for achieving an even tan while minimizing skin damage.
2. The Role of UV Index
The UV index serves as a helpful guideline for those seeking the optimal tanning environment. This numerical scale, which ranges from 0 to 11+, indicates the strength of UV radiation on a given day. Generally, a UV index of 3 or higher is suitable for tanning purposes. Conversely, low UV index readings may not provide adequate levels of light for effective tanning, leading to prolonged exposure without tangible results. Monitoring the UV index can therefore prevent unnecessary skin harm.
3. Time of Day Matters
The diurnal cycle imposes significant variations in UV radiation. Midday—particularly between 10 AM and 4 PM—often showcases the highest levels of UV exposure. This peak time provides a more concentrated dose of UVA and UVB rays, facilitating a quicker tanning process. However, one must tread carefully, as the intensified rays also heighten the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage. Early morning or late afternoon sun can be advantageous for leisurely tanning sessions with reduced risk.
4. Geography and Altitude
Geographical location significantly influences UV exposure and, by extension, tanning ability. Areas closer to the equator experience more intense UV radiation year-round compared to regions farther north or south. High-altitude locales also elevate UV intensity; the thinner atmosphere allows for increased UV penetration. Thus, adventurous spirits basking in the sun at higher altitudes may find themselves tanning more effectively than their sea-level counterparts.
5. The Cumulative Effect of Tanning
It’s crucial to remember that tanning is not an instantaneous process. The skin builds up its melanin over time, leading to gradual color changes. Overexposure in one session may result in an immediate tan; however, it can also trigger subsequent sunburn, delaying the overall tanning process. Adopting a systematic approach with short, controlled exposure durations allows the skin to adapt and darken gradually without detriment.
6. The Myth of “Safe” Tanning
Despite the desire for a bronzed complexion, the paramount concern remains skin health. Many individuals cling to the myth of “safe tanning,” believing that one can avoid harm through occasional sun exposure. However, the reality is that any exposure to UV radiation can elicit skin damage, cumulative over time. According to dermatological perspectives, using sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak hours are essential to counteract the dangers while still enjoying the sun.
7. Artificial Tanning Options
For those wary of UV exposure, artificial tanning options abound. Tanning beds emit concentrated UVA rays and can result in a quicker tan; yet, they pose similar, if not greater, risks of skin cancer due to their high-intensity output. Alternatives such as self-tanning lotions and spray tans offer a pigment-rich hue without the need for UV exposure, providing a guilt-free approach to achieving a sun-kissed glow. Balancing aesthetics and safety has never been easier.
8. Skin Type Considerations
Individual skin types play a crucial role in determining tanning efficacy and safety. Fair-skinned individuals, possessing less melanin, are more susceptible to sunburn; hence, they should initiate tanning sessions with shorter durations and increased protection. Conversely, darker skin tones may tan more uniformly and rapidly. A nuanced approach to tanning, tailored to one’s skin type, is vital in ensuring not only a desirable complexion but also the preservation of skin health.
Conclusion
The quest for the ultimate tan intertwines with various factors, including the nuances of UV radiation, timing, geographical variations, and individual skin types. Understanding these elements fosters a more strategic approach to tanning, leading to beautiful results while safeguarding skin health. Embrace the sun, apply knowledge wisely, and illuminate your summer days with the glow of a well-tanned complexion, all while cherishing your skin’s well-being.









Leave a Comment